
The SNMP protocol is used for providing and transferring management information within the network environment. The SNMP protocol is used for communication between the management stations and the agents. The management information is stored in Management Information Bases (MIB).
As a network agent utilizing SNMP, the IB-2x provides the standard MIB-II and a private MIB stored in the interface card. The private MIB stores all interface card parameters and status information.
When using SNMP, make sure that:
The IB-2x SNMP parameters may be configured using AdminManager. Should an error occur such as 'Add Paper,' the IB-2x printer can automatically generate a ‘trap’, an error message sent to pre-determined trap recipients. In SNMP terminology, a ‘trap’ refers to an unsolicited notification of an event by the managed device (i.e. the IB-2x). Traps may be used by a management application as an alternative to polling a device to determine its status, however, the management application must be capable of receiving SNMP traps.

| Read Community | The Read Community can be used like a password. When a management application sends an SNMP request to read a value, it must include the correct Read Community name or the request will be rejected by the IB-2x. | |
| Write Community | Similar in function to the Read Community, but used in SNMP requests to write (change) a value. | |
| sysContact | The MIB-II sysContact object, usually the email address of the network administrator. | |
| sysName | The MIB-II sysName object, usually the host or domain name of the IB-2x. | |
| sysLocation | The MIB-II sysLocation object, usually the location information of the IB-2x printer. | |
| Enable Authentication Traps | Check to enable or uncheck to disable the MIB-II EnableAuthenTrap object. If enabled, an SNMP trap is generated when an attempt to read or write is made using an incorrect community name. The trap is sent to the configured trap address. |
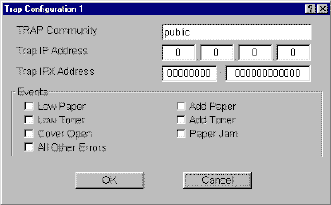
| TRAP Community | The SNMP trap community name to be used when the IB-2x generates a trap. | |
| Trap IP Address | The IP address which will receive the trap. | |
| Trap IPX Address | The IPX address which will receive the trap. | |
| Events | Select the events which will cause a trap to be generated. |