
This
section describes several methods for configuring the IB-2x IP address
information. The method you use will depend on your particular network
configuration as well as your personal preferences. For example, if your network
includes a DHCP server, then you will likely use DHCP for setting the IB-2x IP addresses. Following are the possible methods for configuring
IB-2x IP
addresses:
After following the procedures in this section to
configure the IP address, it is recommended to verify the IP address settings:
You can directly enter the IP address, gateway address, and subnet mask address using the menu system from the operator panel. The following procedure is applicable to virtually all Ecosys printers except those having no operator panel.
To set the IP address information, proceed as follows:
Interface >
Option
If the above does not show 'Option,' press ENTER. Press the + key repeatedly until it shows Option. Then, press ENTER again.
>TCP/IP >
On
>>IP Address
000.000.000.000
>>Gateway
000.000.000.000
Using the same manner as 7. above, complete the gateway address. Press ENTER.
>>Subnet mask
000.000.000.000Using the same manner as 7. above, complete the subnet mask address. Press ENTER.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) provides a mechanism for delivering IP configuration parameters, including IP address, subnet mask, etc. to devices on an IP network. DHCP alleviates the administrative burden of managing individual IP addresses.
A DHCP server processes IB-2x DHCP discovery broadcasts and returns an IP address to the IB-2x. The DHCP server may be set up to grant an IP address for a limited time (a temporary lease) or for an unlimited (an unlimited lease), or it may be configured with a permanent address reservation for the IB-2x.
Unlimited Lease or
Address Reservation in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000
In Windows NT and 2000, lease duration is set for a particular scope, or group of addresses. Thus, lease duration should be set to Unlimited for the scope to which the IB-2x belongs. If this is not desired, then the IB-2x should be defined as a Reserved Client.
Use the following procedure in Windows DHCP Manager to add a reserved client.
Select the scope that the IB-2x will belong to, then select Add Reservations from the Scope menu. The Add Reserved Clients window will open.

In Figure 1, enter the IB-2x Ethernet address (Do not enter the colons, e.g. '0080920010ea.'), IP address, and other information. The IB-2x Ethernet address may be obtained from the IB-2x Network Status Page.
Click Add.
Turn printer power on. The printer receives the IP address from the DHCP server. You can print the network status page to confirm the IP address.
Verifying the Active Lease Status
You can verify active leases for a particular scope by opening the Active Leases windows:
From the Scope menu, select Active Leases. Reserved clients will display "Reservation" or "Reservation in use" beside the client name.

Disabling DHCP
If IP address assignment with DHCP is not desired, it may be disabled using the IB-2x Quick Setup wizard, the printer front panel, a web browser, or several other methods.
IMPORTANT: Note, however, that DHCP IS
AUTOMATICALLY DISABLED when the IP address is set using any other method such
as the Quick Setup wizard, printer front panel, etc.
IP Address Persistence
When the printer is turned off and back on will the IB-2x retain its IP address?
| Temporary |
If a temporary lease is obtained from a DHCP server, then the IP address is temporary. That is, when the printer is turned off and back on, the IB-2x does not begin using its IP address until it has negotiated with a DHCP server. Thus, if a DHCP server is not available, the IB-2x will not have an IP address. This is necessary to prevent IP address conflicts in a DHCP environment. |
| Permanent |
If an unlimited lease or address reservation is obtained from a DHCP server, or
if set by any method other than DHCP, then the IP address is permanent. That is,
when the printer is turned off and back on, the IB-2x will begin using its
assigned IP address. |
WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) is used by Windows NT to provide a mechanism for mapping the NetBIOS name, commonly referred to as 'host name,' to an IP address. WINS requires a Windows NT or Windows 2000 server to be configured as a WINS server.
WINS enables defining a printing configuration which references the printer by its name rather than by its IP address. Thus, even if the printer IP address is changed via DHCP, the printing configuration will still be valid and printing will continue uninterrupted. Another advantage of WINS is that a new printer may seamlessly replace an old printer simply by:
WINS Registration and Naming
The IB-2x must be given the address of the primary WINS server where it will register its host name. It may optionally be given the address of a secondary WINS server. The DHCP server is often setup to provide the IB-2x with its host name and the WINS server addresses. Refer to your DHCP server documentation for the proper setup procedures.
Alternatively, the following AdminManager procedure may be used to configure the host name and WINS server addresses:

You may also optionally enter:
WINS registration may be verified by printing the IB-2x Network Status Page. Once the IB-2x has successfully registered with a WINS server, the WINS Status will show as Registered in the TCP/IP section.
You can enter the IP address information using the Advanced Setup option on the IB-2x CD. Advanced Setup installs the AdminManager program for advanced IB-2x configuration options (Advanced Setup also allows running AdminManager directly from the CD).
Run the IB-2x AdminManager.
To run AdminManager, see Installing the IB-2x AdminManager.
From Setup, select Enter Initial IP Address. The IP Address Setup window opens.

In Ethernet Address, enter the Ethernet address of the interface card, e.g. '00 c0 ee 10 00 0d.' The Ethernet address is physically labeled on the back of the interface card and is also printed on the Network Status Page.
In IP Address, enter the IP address to allocate for the interface card, e.g. '192 168 110 171.'
Click OK.
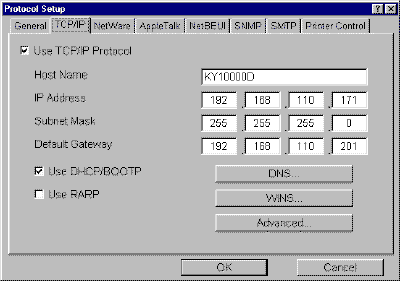
Once the IP address is configured, the rest of the IP address information can also be entered by AdminManager:
From the Setup menu, select Protocols, and click the TCP/IP tab.
Enter the Subnet Mask address.
Enter the Default Gateway address.
Click OK.
You can resolve the IP address via RARP or BOOTP over the Ethernet connection. The host computer must support either protocol as the boot server. The address information will be stored in a configuration file on the server as, for example, ethers or bootptab file. The interface card issues each time the printer is turned on RARP and BOOTP requests and attempt to receive the configuration information returned by the server.
To prepare a configuration file for BOOTP:
Properly connect the printer to the network.
Create and store the configuration information in a /etc/bootptab file.
For example, to set '192.168.20.28' for IP address; the hardware address is '00:80:92:00:10:ea,' enter as follows:
ht=ether:\ #Target hardware type ha=0080920010ea:\ #Target hardware address ip=192.168.20.28:\ gw=192.168.20.254:\ #Default gateway address sm=255.255.255.0:\ #Subnet mask
In /etc/inetd.conf, add:
bootps dgram, udp wait root /etc/bootpd bootpd
Reset inetd by:
kill -1 1
Turn printer power off, then on.
The printer automatically issues BOOTP requests to the server and receives the BOOTP response to obtain the configuration information.
To prepare a configuration file for RARP:
Properly connect the printer to the network.
Create and store the configuration information in a /etc/ethers file.
For example, to set '192.168.20.28' for IP address; the hardware address is '00:80:92:00:10:ea,' enter as follows:
00:80:92:00:10:ea 192.168.20.28
Start RARPD on the workstation. Enter:
rarpd -a
Turn printer power off, then on.
The printer automatically issues RARP requests to the server and receives the response to obtain the configuration information.
The RARP information the server returns contains only the IP address. Therefore, you must use another method, such as the printer's operation panel or AdminManger, to set the subnet mask and gateway addresses.
ARP is available for resolving IP addresses both in Windows and UNIX networks. The IP information can be set by registering it in the ARP table.
Using the 'arp' Command and 'ping' command
arp -s 192.168.20.28 00:80:92:00:10:ea tempUnder Windows95/98, Windows NT, at the DOS prompt:
arp -s 192.168.20.28 00-80-92-00-10-eaThis procedure only 'registers' the IP address in the ARP table and does not 'write' it in the interface card. Perform the following step.
ping 192.168.20.28
Print a network status page to verify that the IP address information has been properly set
The network status page will also be useful during diagnostics on network problems.
To print a network status page, press the STATUS key on the printer's operator panel. The network status page ('NETWORK STATUS PAGE') will be printed following the printer's normal status page ('STATUS PAGE').